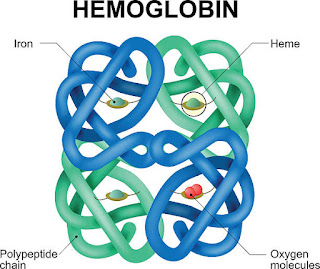
Introduction of blood Blood (Introduction and Composition) Definition : Blood is specialized connective tissue consisting of liquid intercellular substance plasma and formed element RBCs , WBC, and platelets. It circulate in closed system of blood vessels and provides a medium to transport substances from one part of the body to the other. pH of blood 7.4 Range 7.35 to 7.45 Limits Not lower than 6.8 and not more than 7.8 pH of RBC 7.1 (less alkaline) composition of blood. I) formed element: 45% cellular part RBC , WBC, and platelets. II) plasma (fluid part) 55%: 1) water 91 to 92% 2) solids= 8 to 9% a) in-organic: sodium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, copper and iron b) organic i) proteins serum albumin 4.5% serum globulin 2.5% fibrinogen 0.3% prothrombin, etc ii) Non protein: nitrogenous substances, eg urea, uric acid, creatinine, NH3 and amino acids etc iii) fats neutral fat, phospholipid, choleste...