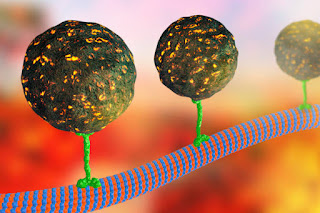
Cytoskeleton (Microtubules,Intermediate Filament,Microfilament Cytoskeleton : skeleton of cell maintain the structure of cell. permits the cell to change shape and move. Cytoskeleton composed of microtubules,microfilaments and intermediate filaments. microtubules they are long unbranched and slender structure. ==> Road inside cell for transportation. Made up of two Globular protein,Alpha tubulin and beta tubulin,they are involved in the formation and degeneration of spindle during cell division. = = > Several cell organelle are derived from microtubules,these organelles are cilia,flagella,basal bodies and Centriole. ==> They provide the tracks along with several different molecular moters move,transport vesicle, organelles such as secretary granules and mitochondria . ==> The anticancer paclitaxel (taxol) binds to microtubules and make them so stable so that organelles can't move, mitotic spindle can't form and the cell die. ==>